
Embedded finance is transitioning from being a mere concept to a force that could substantially influence our evolving financial services landscape. Among embedded forms of payments, lending, and insurance, both embedded investments and wealth are expected to play pivotal roles, offering insights into future developments in personal finance. This Viewpoint examines the wider topic of embedded finance from multiple lenses and delves into the origins, evolution, and prospective trajectory of embedded investments and wealth, highlighting the intertwined relationship with embedded savings.
ORIGINS & RISE OF EMBEDDED FINANCE
The foundation of embedded finance lies in the marriage between finance and technology. Before the digital revolution, traditional banking and finance were compartmentalized, usually operating in isolation. As technology moved into every facet of our lives, these barriers began to erode. Fintechs began offering banking services, while banks started leveraging technology to expand their scope of service. This convergence laid the foundation of evolving from standalone finance to integrated finance to embedded finance (see Figure 1).
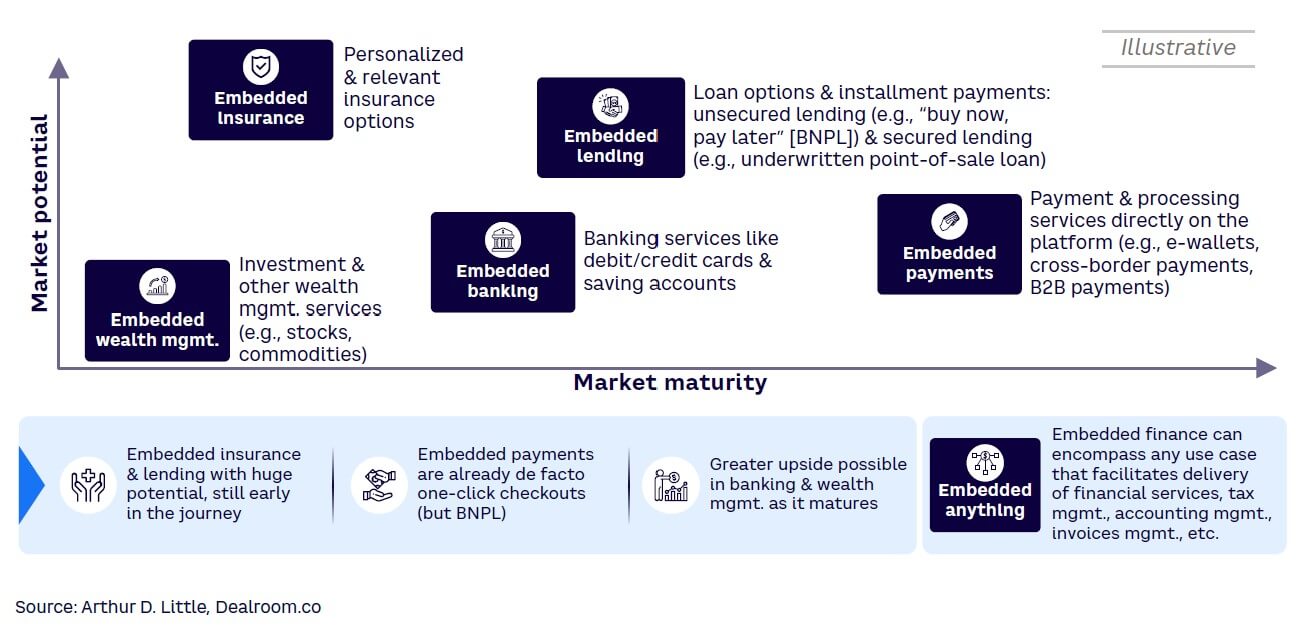
Embedded investments is where accumulated savings are intelligently channeled — not toward spending in the future (we will cover the concept of “save now, buy later” in an upcoming Viewpoint) but rather on creating wealth. Embedded investment platforms take saved funds and direct them into investment avenues, offering returns and increasing wealth. This converts passive savings into active wealth growth, often with minimal input or expertise from the user. The potential for embedded wealth is vast. As of 2022, the global embedded finance market was estimated to reach US $385 billion by 2029. The subset of embedded investments holds a considerable share of that market opportunity.
By providing streamlined wealth management tools, this segment attracts not only seasoned investors but also novices, expanding the market base.
INTERPLAY BETWEEN EMBEDDED SAVINGS & EMBEDDED INVESTMENTS
In a world where finance is intertwined with daily digital experiences, embedded savings is the silent gatherer, while embedded investments is the astute grower, turning pennies into portfolios. Within embedded finance, two facets are proving particularly interesting: embedded savings and embedded investments. Their interplay, though subtle, has the potential to redesign how consumers approach money management, creating a frictionless pathway from saving to investing:
-
Embedded savings — the gateway to financial prudence. Often likened to digitally enhanced piggy banks, embedded savings platforms give users a way to seamlessly integrate savings mechanisms into their routine digital transactions. The psychology behind it is straightforward: simplifying the act of saving by integrating it into daily activities, reducing decision fatigue and making savings almost involuntary.
(In the Viewpoint, “From Micro-Saving to Big Impact,” we shared our perspective on this topic.) At its core, embedded savings is about integrating savings tools within nonfinancial platforms. Imagine you’re purchasing a coffee through a mobile app. The coffee costs $3.65, but you’re charged $4. The extra $0.35 is automatically diverted to a savings account or fund. Such tools take advantage of daily transactions, transforming mundane activities into financial opportunities. This “spare change” strategy is an effortless way to accumulate significant savings over time. Note that one of the pillars supporting embedded savings is behavioral economics. Research shows that the act of saving money, especially when done consciously, can be mentally taxing for individuals. Decision fatigue, a phenomenon in which making decisions becomes harder with the sheer number of choices, comes into play with traditional savings. Embedded savings eliminates the need for such decisions by automating the process.
-
Embedded investments — turning savings into wealth. Embedded investments leverages the funds you’ve accumulated for wealth generation. Once a savings threshold is reached, these platforms automatically invest the accumulated amount into predefined or personalized investment portfolios, ranging from conservative bonds to mutual funds or more aggressive stocks. The idea is not just to save, but to make the saved money work for the user, compounding over time.
The key is the seamless flow between embedded savings and embedded investments. The journey from a user’s daily digital activity to saving and, subsequently, to investing is integrated, eliminating the need for active financial planning or management. It’s a passive, yet effective, way to manage and grow one’s finances.
MAKING MAGIC HAPPEN
Embedded wealth: The next phase of fintech disruption
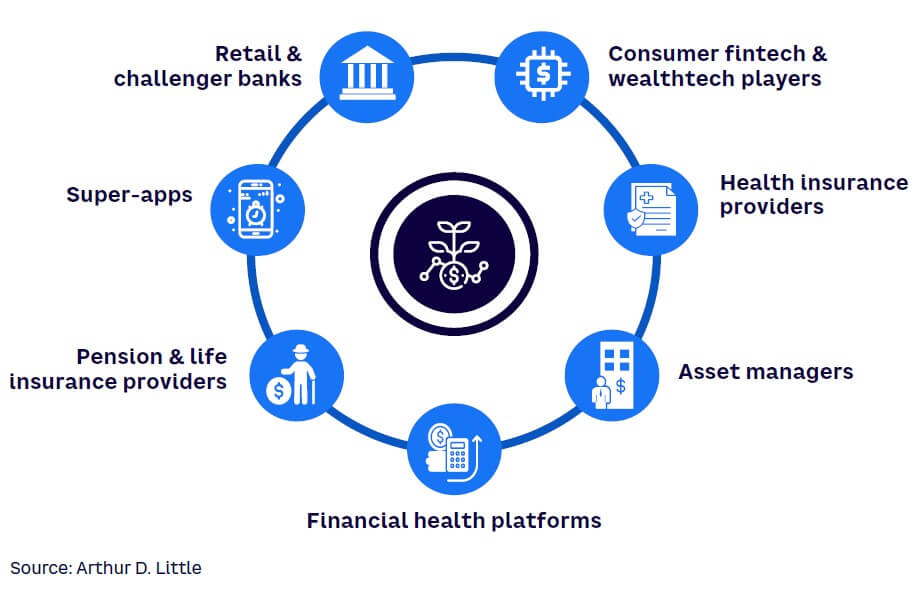
Embedded wealth services can be offered through a wide range of platforms ranging from neobanks to super-apps (see Figure 2). Some of the players growing their embedded wealth services rapidly include traditional and challenger banks, asset managers, and super-apps.
Regardless of the use case and/or the providers, the embedded wealth management market is growing and largely untapped. When facilitated by an established and trusted embedder, it is quicker, easier, and cheaper to offer to an existing customer base.
From daily activities to wealth accumulation
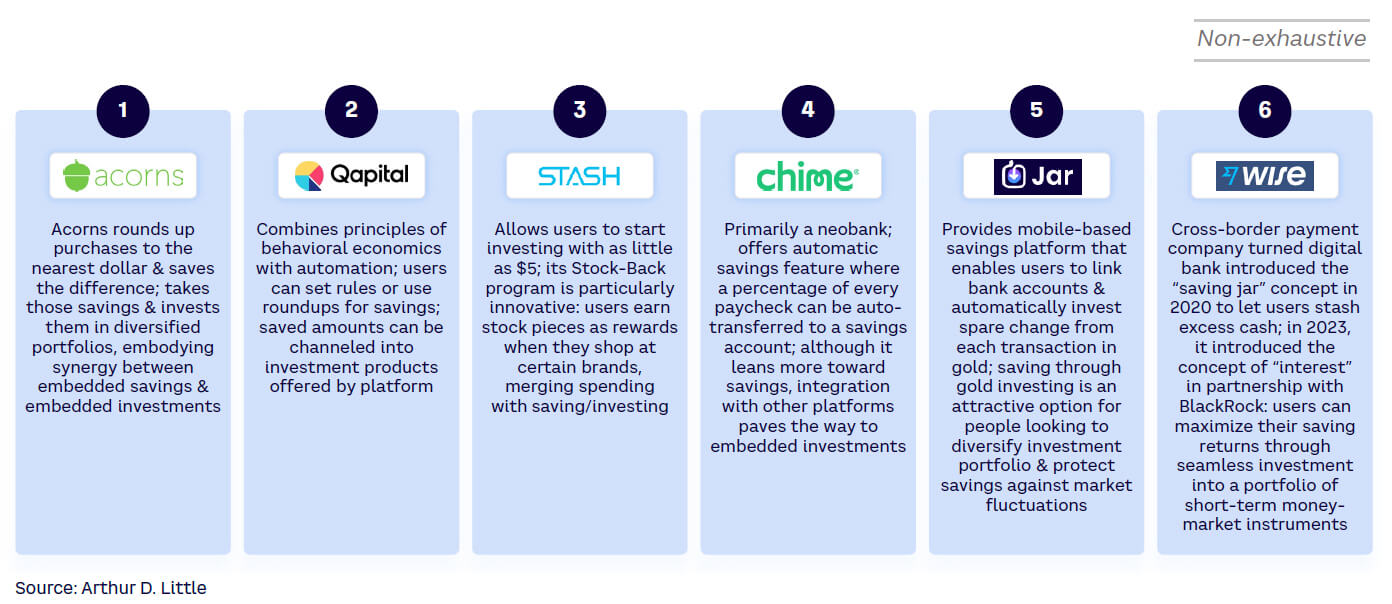
The magic happens when embedded savings and investments operate in tandem. This combination transforms everyday transactions into wealth-accumulation opportunities. Platforms like Acorns exemplify this. In an example touched on earlier, users spend on routine transactions, the platform rounds up the expenses, and the spare change is invested in diversified portfolios. The user’s journey from spending to investing is frictionless — a seamless financial continuum. There are several embedded savings and investments offerings, each looking to deliver a direct path from daily activities to wealth accumulation (see Figure 3).
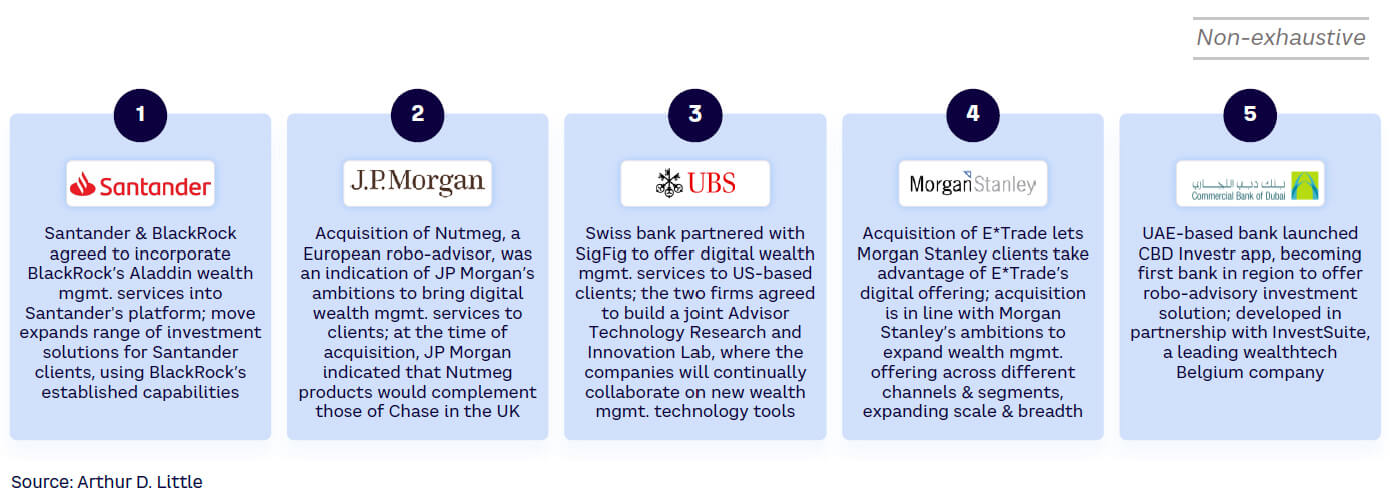
These types of offerings are not limited to neo/digital banks and/or fintechs. Increasingly, incumbent banks are either partnering with wealthtech platforms and/or developing their own embedded wealth proposition (some through M&A). Also, this phenomenon is global in nature; prominent examples include Santander, JP Morgan, UBS, Morgan Stanley, and CBD, among others (see Figure 4).
EMBEDDERS’ OPPORTUNITY
Most embedders (typically nonfinancial institutions with direct access to customers and the necessary level of trust among their target customers) have been focused on embedding payments, as well as lending and insurance. Few have genuinely focused on the opportunity associated with embedded investments.
There are various paths, encouraging varied thinking:
-
Monetization opportunity. Embedders can harness new revenue streams, either through commissions, subscription fees, or a percentage of assets under management.
-
Increased user engagement. Offering financial services can increase the time a user spends on a platform, leading to higher engagement and potentially more revenue from other channels.
-
Value addition. By providing financial tools, platforms can increase their value proposition, making them indispensable to users.
-
Cross-selling opportunities. Users who adopt embedded wealth tools might be more inclined to use other services offered by the platform, increasing overall revenue.
-
User data insights. Access to financial habits can provide invaluable insights into user behavior, which can be leveraged for personalized marketing or service offerings.
-
Customer retention. Providing a suite of services, including financial management, can create stickiness, reducing the likelihood of users switching to competitors.
-
Competitive differentiation. In a crowded digital marketplace, offering embedded wealth services can set a platform apart from competitors.
Most of the rationale listed above is similar to reasons for embracing the wider topic of embedded finance, but the difference lies in the customer journeys they power — allowing them to unlock embedded wealth and investments opportunities. Examples include:
-
Online shopping. Platforms like Amazon and Noon could offer investment options based on amounts saved through discounts or allow users to invest their cashback rewards.
-
Social media platforms. Users on sites like Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and even Linkedin could be presented with investment options based on their likes, follows, or online behavior.
-
Travel booking portals. Users booking flights or hotels could invest amount saved from deals or discounts.
-
Utility bill payments. Utilities could offer investment suggestions based on monthly savings on utilities.
-
Online subscriptions. Media platforms like Netflix and Spotify could provide investment options proportionate to subscription fees.
-
E-learning platforms. Users could be invited to invest in educational savings plans or related financial products.
-
Food delivery apps. Apps like Deliveroo, Jahez, UberEats, and DoorDash could present investment options based on savings from promotional deals.
-
Fitness and health apps. Users reaching fitness goals could be presented with options to “invest” in health insurance or related financial products.
-
Gaming platforms. Gamers could be presented with real-world investment options based on virtual in-game earnings or achievements.
-
Freelance job portals. Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr could offer freelancers options to invest part of their earnings directly into diverse financial products.
Almost every online interaction or transaction (and some offline ones) presents an opportunity for embedded wealth services, given the right context and a user-centric approach. The goal is to blend financial decisions seamlessly into everyday online activities, making wealth management intuitive and habitual.
CHALLENGES & THE ROAD AHEAD
The synergy between embedded savings and investments is compelling, but the path isn’t devoid of hurdles (see Figure 5). Among several challenges, a few showstoppers range from educating and attracting customers, managing technology (data security, scaling, and integration), and building a profitable business model (finding the right partners and designing the right revenue model).
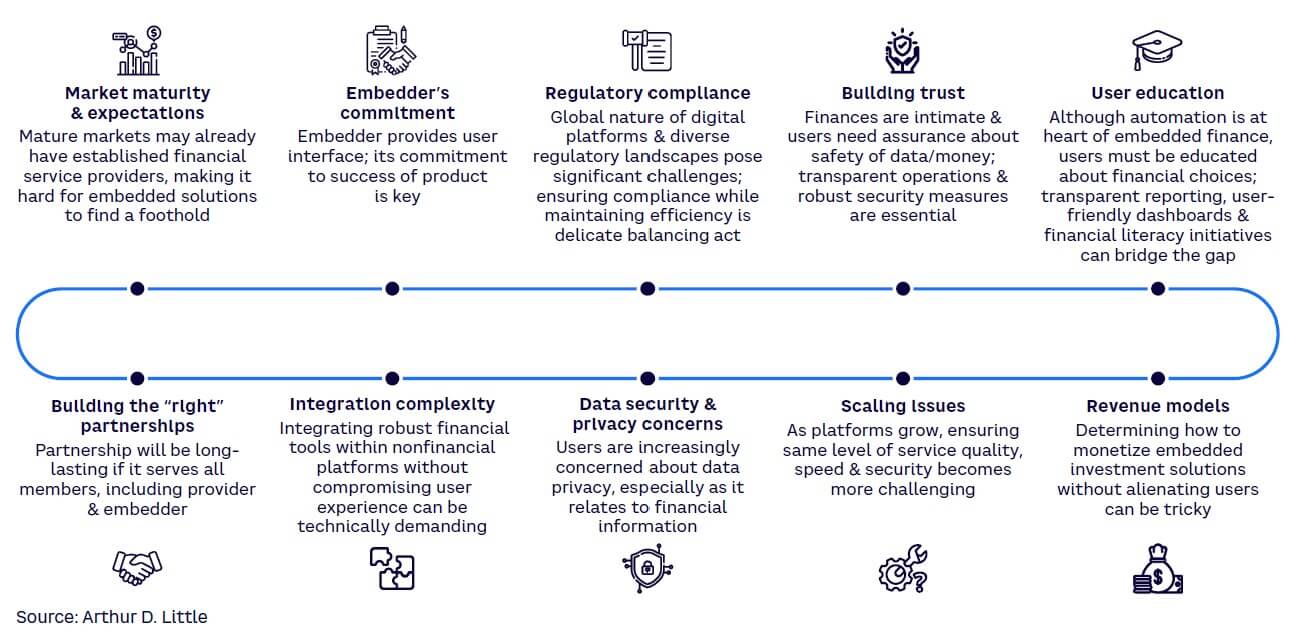
This list may seem daunting, but a number of successful players in the domain like Qapital have navigated these challenges by combining behavioral economics with technology to enable goal-oriented savings and investments that resonate with user aspirations. Qapital’s success story should serve as an inspiration to new companies entering this space.
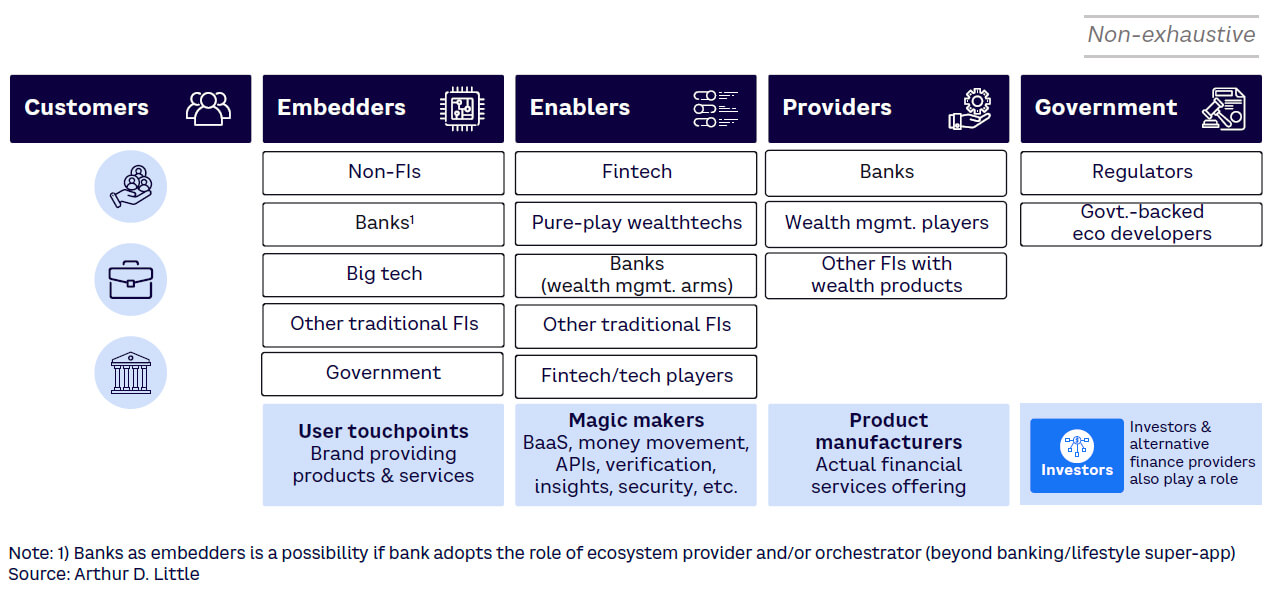
ROLE OF STAKEHOLDERS
The embedded finance ecosystem comprises a variety of stakeholders, each playing a distinctive and significant role (see Figure 6). To make the magic happen, stakeholders across the value chain must do their part and do it in tandem:
-
Customers. End users stand to gain the most, enjoying seamless financial management and potential wealth accumulation. Their feedback, preferences, and trust shape the industry.
-
Embedders. Platforms that integrate savings and investment tools need to ensure user-centric design, regulatory compliance, and continuous innovation.
-
Enablers. As the technology backbone, these companies must ensure robust, secure, and scalable solutions while staying abreast of financial trends and user behaviors. They are the glue that holds everything together.
-
Banks, traditional wealth managers, and other financial institutions. Their expertise, established trust, and vast resources make them invaluable. However, they need to adapt, innovate, and collaborate to remain relevant.
-
Regulators. These entities must frame guidelines that protect user interests while fostering innovation.
Conclusion
GLIMPSING THE FUTURE
Embedded savings and embedded investments are the dual engines powering the modern consumer’s financial journey — one accumulates, the other multiplies, both seamlessly integrate into everyday digital life. With technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain gaining momentum, we can expect hyper-personalized financial solutions, more diversified investment avenues, and possibly a convergence of embedded finance components into unified platforms. As embedded finance permeates more sectors, we can see scenarios in which smart devices not only facilitate savings but make investment decisions based on behaviors, preferences, and financial goals.
The embedded wealth phenomena reflect how future digital investment and wealth services will be consumed. With a market potential of billions of young, digital-savvy consumers who use their mobile phones for everyday digital financial services, including digital wealth, financial institutions and embedders worldwide should not only take note, but they should also take action.
The journey from the compartmentalized world of traditional finance to the integrated realm of embedded investments and wealth is a testament to the transformative power of rapidly emerging technology. As embedded savings and investments continue to collaborate, they pave the way for a future where financial growth is an integrated aspect of our digital existence. For stakeholders, the message is clear: adapt, collaborate, and innovate to get ready for entwined finance.



