
Banks are evolving by leaps and bounds, using digital channels to facilitate interactions and meet the demands of their customer base. In this context, the bancassurance model — which has been an example of success in past decades — must adapt to changing customer requirements and seek ways to continue growing. In this Viewpoint, we explore some options bancassurance businesses can initiate to help them thrive and capture the digital sales opportunity.
SETTING THE STAGE: THE NEED FOR A DIGITAL SALES STRATEGY
The evolution of the banking industry is ongoing. Banks have moved from implementing digital channels toward developing a fully omnichannel experience for their customers. This technology-centered landscape is more important than ever; the vast majority of today’s customers demand a digital presence from companies they support. A smaller yet significant proportion of clients are transitioning from brick-and-mortar to online. There has been an undeniable shift by banks toward improving and adapting their digital channels to make them both user-friendly for customers and a highly intuitive tool to drive sales.
Nevertheless, expanding a bancassurance business goes beyond building digital assets; implementing an omnichannel strategy can create a seamless, integrated experience for customers, regardless of which channel or device they use to interact with their bank. This strategy is based on:
-
A consistent, real-time user experience (across all channels, including web, mobile, and in-person) which is cohesive, easy to navigate, and ensures that customer data is shared across channels and accessible for any interaction, giving the customer the opportunity to switch between channels/devices.
-
The use of data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) to provide personalized product recommendations, promotions, and offers across all digital channels.
-
The application of AI as a game-changer for automation and simplification, which improves support and interaction and upgrades underwriting tasks, making them more efficient and accurate.
If they do not want to be left behind, bancassurance businesses must reinvent themselves to capture digital opportunities, using current interactions with their customers to realize the potential that flourishes around their existing relationships.
This Viewpoint focuses on an end-to-end digital path strategy to improve bancassurance sales. We start by defining the types of digital customers to target and their main characteristics. Then we identify the optimal tactics for reaching them via a fully multichannel approach.
DIGITAL BANCASSURANCE MODELS
Although all companies have their own unique attributes, Arthur D. Little (ADL) has identified three types of digital customers and developed generic but experience-based descriptions for them. ADL’s previous work informed the decisions about which models best suited each type of customer in order to maximize conversion rates while ensuring positive customer experiences.
All three types of digital customer have specific traits:
-
Engaged customers — identified based on their recurring interactions with their bank, which is typically their main one.
-
Dormant customers — have limited interactions or none at all with their bank, which is typically their secondary bank.
-
Non-customers — are not part of a bank’s customer base but might be interested in buying insurance.
Widely differing needs and interests among customers call for various methods of gaining their attention and suggesting the right insurance to them. The details below describe the most suitable alternatives for meeting insurance-related customer needs.
APPROACHING ENGAGED CUSTOMERS
Engaged customers are characterized by a substantial number of interactions with their bank; using these moments to offer insurance products is a potentially strong strategy. Leveraging events allows the offer to be made at the right time, maximizing both the conversion rates and the customer experience.
We identified two relevant strategies to convert engaged customers:
-
Embedded insurance sales
-
Contextual insurance sales
Embedded insurance sales
Embedded insurance is the real-time bundling of insurance products during the commercial transaction of another product or service. Bancassurers use this type of sales model by taking advantage of the range of banking customer purposes to offer targeted insurance products. For example, when a client is soliciting a loan, insurance companies can offer payment-protection insurance.
If applied well, this approach results in very high conversion rates since the offer is made in a moment when the customer is more receptive and the coverage is related to the ecosystem of the product or service they are pursuing.
Several requirements must be considered for this sales model to be effective (see Figure 1). First, it is of utmost importance that the different insurance models and actions are aligned with the overall bank strategy, to avoid friction and make the most from combined synergies. Effectively managing leads is necessary. Both businesses need to agree on the rules to define eligible leads, based on the customers’ interests and behaviors.
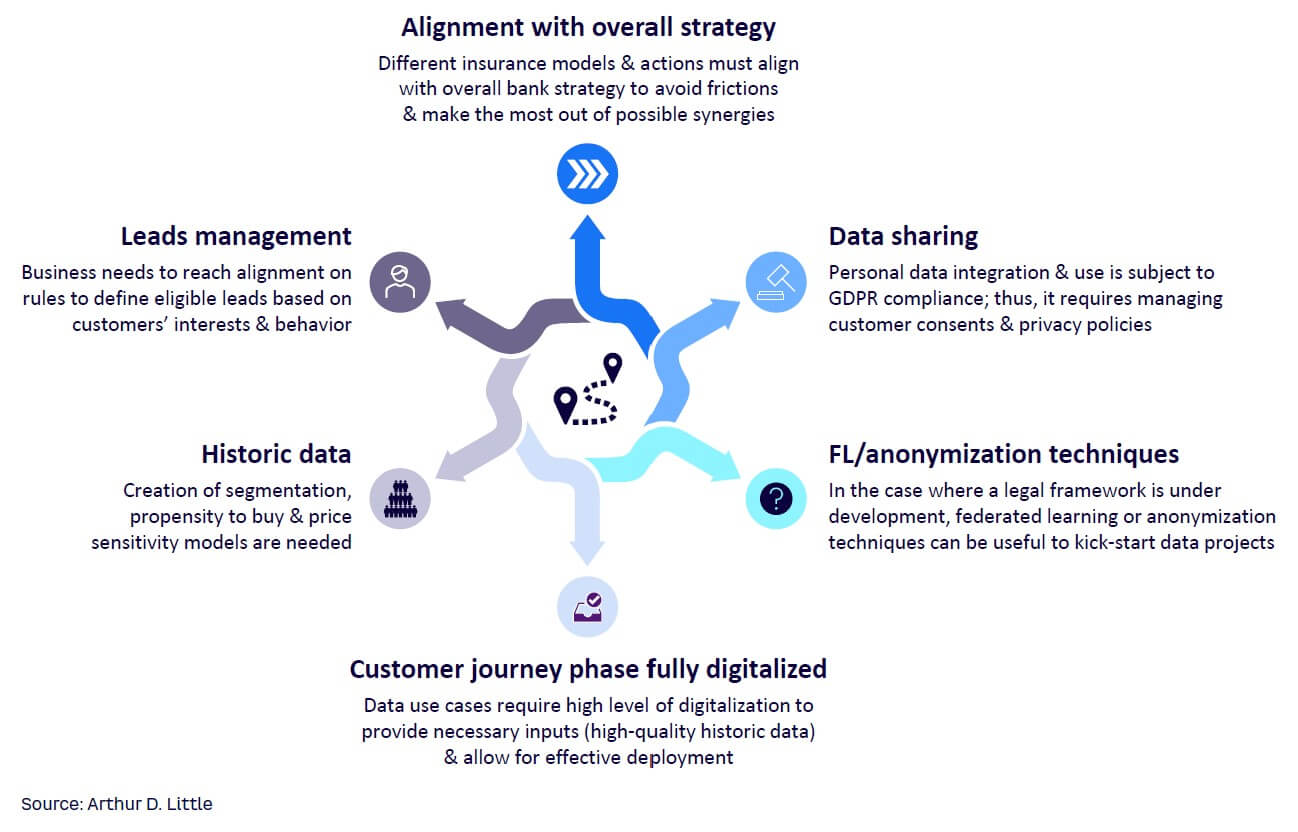
In addition, the entire customer journey should be digitized for optimal results; data use cases require a high level of digitalization to provide the necessary inputs (i.e., high-quality historic data) and allow for effective deployment. Historic data modeling is consequently employed to build models to identify specific products for targeted customers. Examples of models include segmentation, propensity-to-buy, or price-sensitivity models.
Finally, managing customer consents and privacy policies is an imperative for effective embedded insurance sales. In the EU, personal data integration and its use must comply with General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR). If legal framework is under development, federated learning can prevent data exposure and anonymization techniques can be help kick-start data projects.
Contextual insurance sales
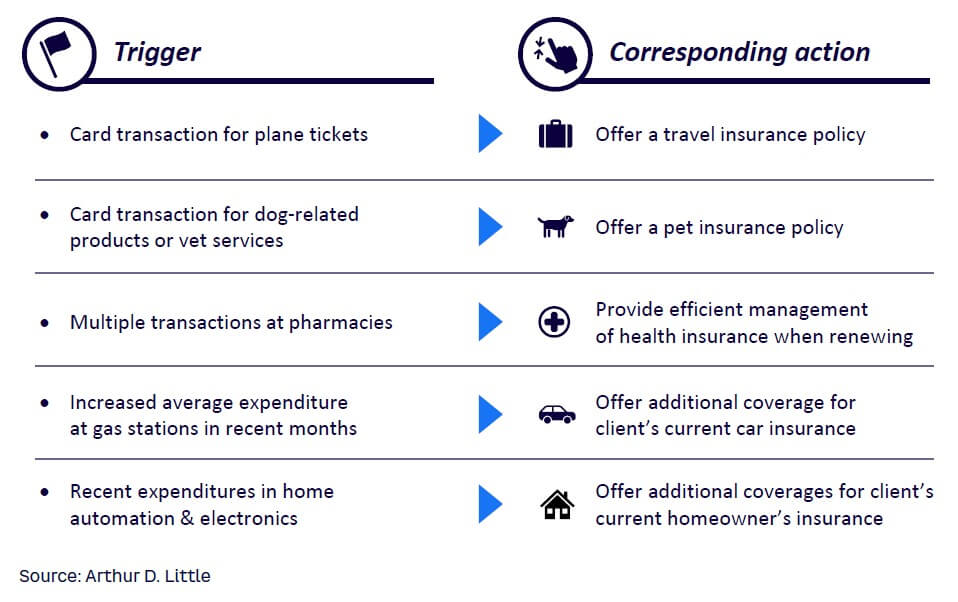
This sales strategy is based on specific triggers and matching them to a set of designated insurance products in near real time. Firms must undergo full data integration to identify the best opportunity windows and recommended actions for each client (see Figure 2). For example, a bancassurance firm could offer a pet insurance policy to a customer with a history of multiple dog-related purchases.
It is important to note that developing and executing contextual action models requires handling personal data and using customer consents to comply with GDPR. A legitimate business interest is not enough for contextual actions. To be effective, bancassurance businesses require effective platform integration, which allows the development of analytic models, combines bank and insurance data, and supports the execution and monitoring of campaigns.
Carrying out near-real-time actions requires direct connections with customer touchpoints (ingest inputs) and the platform (analytic models). Actions triggered by events should be accompanied by other activities from the same phase of the customer journey, such as sales or claims, which should also be digitalized to enhance the customer’s overall experience. This strategy achieves its best results with companies who offer a wide range of products, as this makes the most of the detection and actionability of the different triggers. Finally, businesses need to align their rules to define eligible leads based on customers profiles.
APPROACHING DORMANT CUSTOMERS
Dormant customers are characterized by low levels of engagement with their bank, which means their interactions range from none to very limited.
In this situation, we cannot benefit from the interactions we have with engaged customers to make offers at the opportune moment. Instead, it is vital to find alternative ways that will still convert customers, albeit at lower conversion rates than those of engaged customers because of lower customization.
Two approaches can reach dormant customers:
-
Digital campaigns
-
Standalone marketplaces
Digital campaigns
Greater integration with banking operations can facilitate the use of digital campaigns to connect with existing bank customers. These campaigns use different methods for customer outreach — email, short message services (SMS), app and Web banners, push notifications, and so on (see Figure 3).
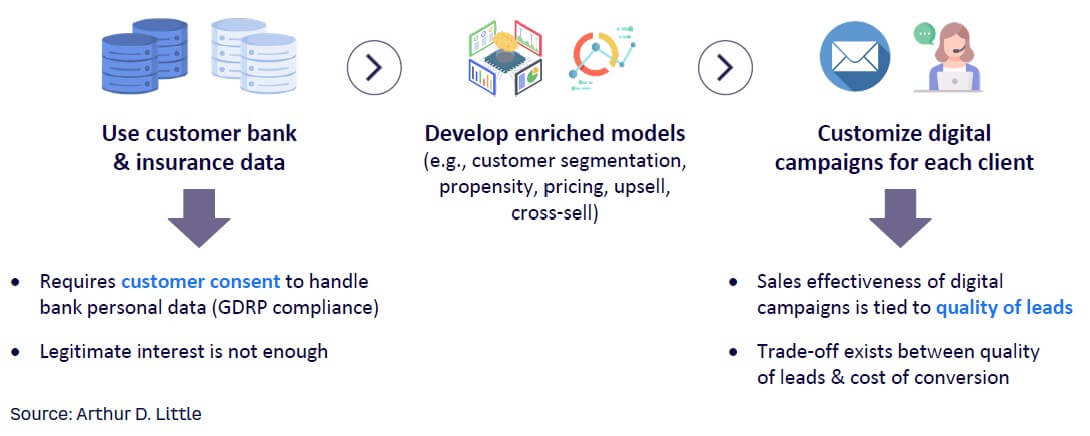
This approach is based on offering products on digital channels based on propensity-to-buy models, which use past purchasing behavior to predict the likelihood of future purchases. Upselling and cross-selling strategies can also be integrated into digital campaigns.
Thoughtful use of customer bank and insurance data forms the foundation of a digital campaign strategy. Data analytics can enrich customer segmentation models, propensity models, and pricing models, which can be used to create media that are tailored to each client. There is a direct trade-off between quality leads and conversion costs, as the sales effectiveness is tied to the quality of leads. An insurance company must collaborate with a bank to prioritize and contact the customers with highest conversion potential.
Extracting the value of this opportunity requires obtaining customer consent. As with contextual insurance sales, legitimate interest is not sufficient for a bank to use customer data to develop models and make customized offers.
Standalone marketplace
Creating a digital insurance store is another alternative with a low level of data integration with banking activity (see Figure 4). The only data shared fulfills the purpose of easing customer navigation online or in the app and pre-filling necessary data to provide a quote or facilitate a subscription.
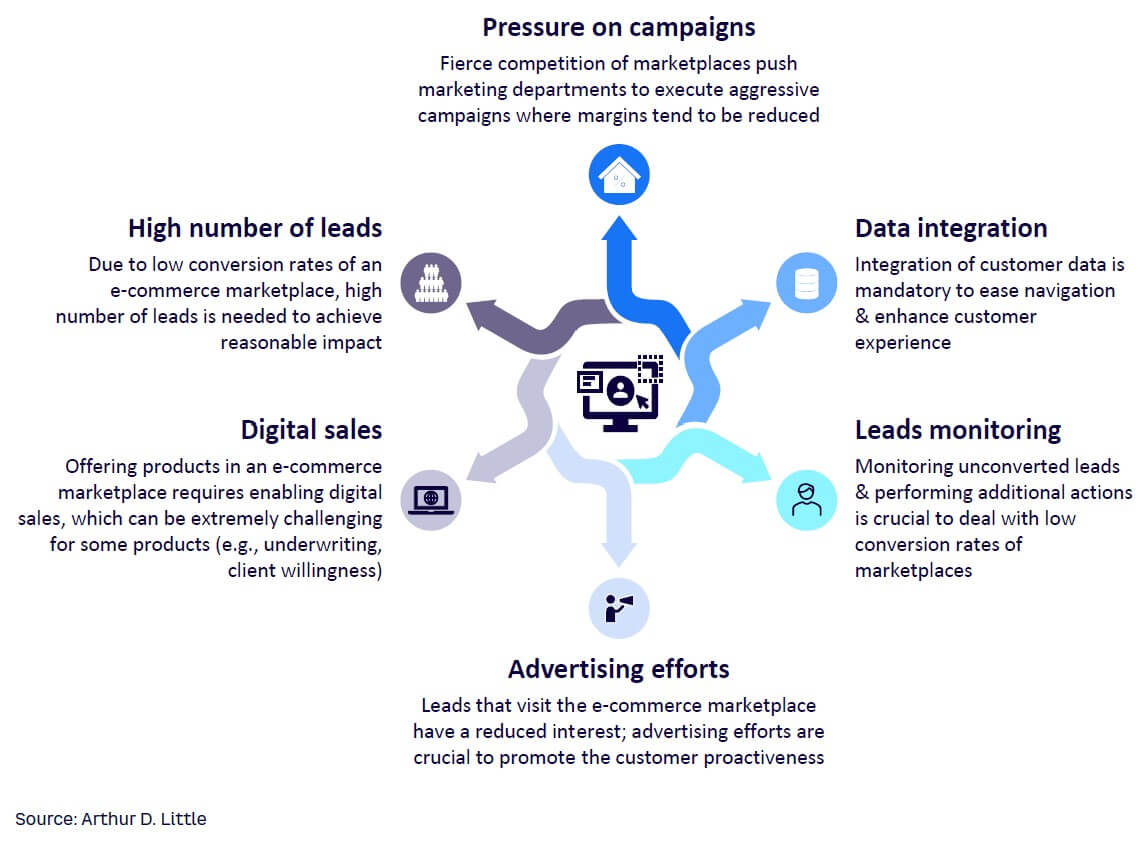
The standalone marketplace model is an option for bancassurance businesses that are not interested in complex data-integration solutions. However, it is less effective compared to other sales strategies, as it requires the customer to be proactive. The investment of effort and time may make a digital marketplace less appealing than other options, and clients may look elsewhere for insurance products. Companies opting for this marketplace model have to be willing to direct greater efforts toward advertising and push their marketing departments to execute aggressive campaigns to promote their products.
Moreover, the low conversion rates of e-commerce marketplaces result in the need for a high number of leads to achieve a reasonable impact. Unconverted leads must be continuously monitored so bancassurance businesses can perform additional actions to build their customer base.
APPROACHING NON-CUSTOMERS
Entering the open market is a recurring challenge for bancassurance businesses since it involves a huge opportunity to broaden the database and multiply the potential market with non-customers (i.e., customers outside of banking leads).
How should bancassurers approach non-customers? This is not a trivial question and calls for profound assessment in order to define the most suitable way to do it. Based on our experience, this assessment should take place around the four axes shown in Figure 5.
Product portfolio
Outside the bancassurance environment, competition is fierce and the need for differentiation and the pressure on price are voracious. It is essential, therefore, for bancassurers to assess and objectively reflect on the products with which they can compete in the context of a competitive market where bancassurance levers such as customer information and the use of relevant touchpoints cannot be used. In a market with such limitations, bancassurers should develop an objective analysis based on market benchmarking about products’ value offer and the key drivers for their success.
The products chosen will also depend on the business model selected. For example, when the decision is made to sell on aggregator websites, the offer should be limited to the mass products included in them (e.g., auto, home), while if the bancassurer opts for direct distribution, the range can be wider.
Furthermore, it is important to differentiate the open market value proposal from the bancassurance one to avoid channel friction. This will lead to different products and pricing adapted to each of the channels (open vs. captive).
Finally, even if the value proposition is different, it is important that bancassurers leverage learnings and capabilities developed in the bancassurance business and apply them to products developed for the open market. Bancassurers thus are able to generate competitive advantages by leveraging current pricing models based on clients’ banking data in the traditional bancassurance business and taking advantage of open banking and differential pricing proposals in the open market context.
Commercial model
There are two commercial model options to consider: aggregator websites and direct distribution. Exploiting aggregator websites requires a segmented acquisition strategy (i.e., targeting profitable customers) and cost-effective products. Bancassurers must meet these two objectives to be competitive as well as profitable. At the same time, the range of products to be offered is limited by aggregator websites’ focus (e.g., auto, home, health).
On the other hand, in direct distribution there is greater flexibility in terms of the value proposition to be offered. However, the success of this alternative will depend on generous marketing expenditures in order to develop search engine optimization and management capabilities to acquire customer leads. Direct distribution also requires an optimized sales funnel with a simple and intuitive process that is, if possible, boosted via telephone actions (e.g., contacting customers who have not completed their purchase and are stuck at a particular sales funnel stage).
Brand
Competing outside the bancassurance environment requires a minimum level of brand awareness and trust (this is particularly relevant for products in the health segment). The branding strategy can also make it possible to avoid friction with the bancassurance channel and to offer additional flexibility to compete in the open market. For example, creating an ad-hoc brand for this environment may allow for a different value offer than for the one offered in the captive context, adapted instead to an environment characterized by competition, price pressure, and low availability of customer information.
Bancassurers must choose between creating a new brand versus using the bancassurance brand. Brand development is costly; therefore, leveraging the bancassurance brand would enable levels of awareness and trust to be achieved in less time and at lower costs.
An alternative that balances the reduction of frictions and flexibility with the minimization of awareness costs is launching the products in the open market under a co-branding scheme with both the new brand and the bancassurance brand.
Economic model
To minimize frictions with the bancassurance business as well as cannibalization concerns, it is essential to design a competitive commissioning model for the bancassurance business regarding sales in the open market.
Although the captive context is far less relevant in the open market sales process than it is in the bancassurance environment, this economic model can be justified by using bancassurers’ back office capabilities for reaching operational scale efficiencies, the bancassurance business brand, and the need for joint financing of costs and investments to develop the opportunity. This point is key to maintaining a good relationship between partners and guaranteeing alignment to further develop the business, both in the captive and open markets.
In summary, to be successful in the open market bancassurers must carefully select products that can compete in this context, devote generous marketing expenditure, and develop the opportunity in a way that keeps partners aligned in developing the business as a whole.
Conclusion
DIGITAL REINVENTION
It is essential that bancassurance businesses develop plans to manage the ongoing digitalization in the banking sector. In this Viewpoint, we explored points to consider for a successful sales strategy:
-
Taking advantage of current customer interactions to heighten customer experience and sales performance levels.
-
Creating an omnichannel presence for an integrated customer experience.
-
Using data analytics, AI, automation, and subscription simplification to build a consistent, real-time user experience personalized to meet customer needs.
-
Understanding the three types of digital customers: engaged, dormant, and non-customers. Each group is unique; the strategy for approaching each customer type and making insurance offers will vary.
The bancassurance business must reinvent itself to stay relevant, capture digital opportunities, and expand to create success for the future.

