
DOWNLOAD
DATE
Contact
The telecom industry is evolving rapidly, simultaneously witnessing the rise of new, advanced network transitions while current technology becomes obsolete. This Viewpoint explores how mobile telecom operators can effectively implement customer migration acceleration programs to optimize operations, migrate customers to advanced networks, and unlock new opportunities in a future-ready telecom landscape.
CURRENT STATUS & TRENDS
In the evolving landscape of technological advancement, traditional mobile infrastructure — namely 2G and 3G networks — is becoming increasingly obsolete. These networks are being systematically phased out across various global regions (see Figure 1). However, the pace of this transformation is not uniform. While developed nations have rapidly transitioned to more advanced networks, regions such as Africa and the Middle East still have considerable ground to cover in the journey to sunset outdated technology.
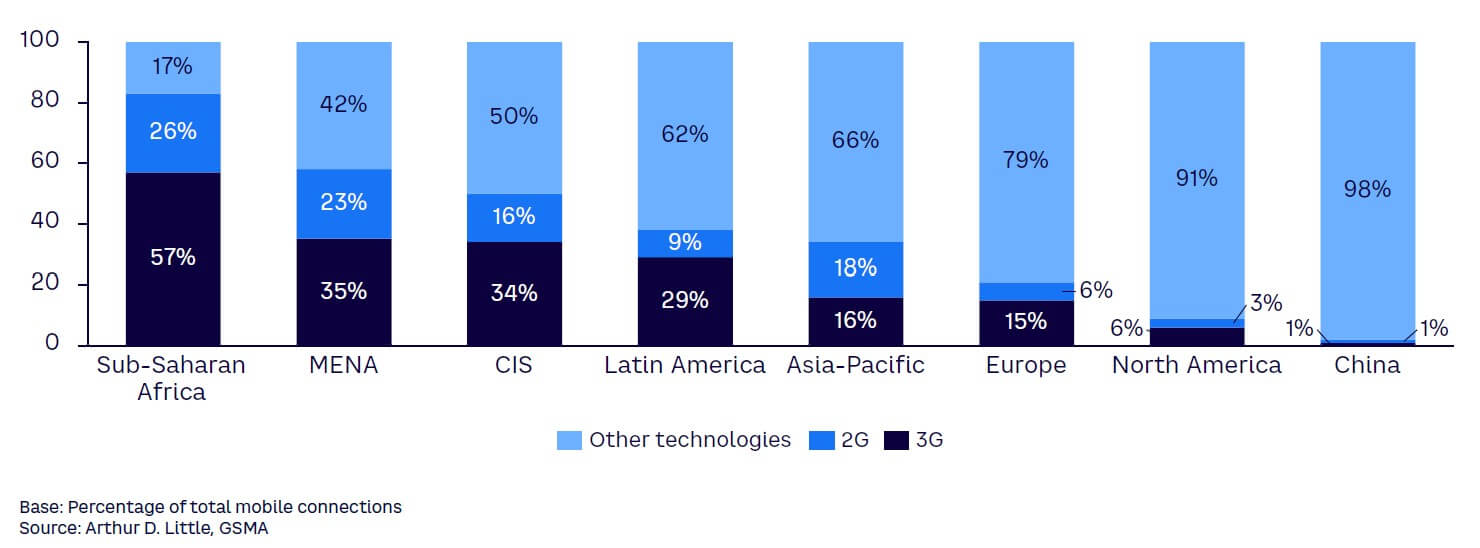
A confluence of factors, including economic disparities, infrastructure limitations, and regulatory challenges, has contributed to this digital divide. In many African countries, for instance, 2G and 3G networks continue to form the backbone of mobile connectivity, due to their wide coverage and the affordability of compatible devices. In parts of the Middle East, similar strides have been made toward adopting 4G and even 5G in urban areas, while rural and remote areas often remain reliant on 2G and 3G networks due to infrastructural and economic constraints.
However, this narrative is changing. The telecom industry in these regions is gradually awakening to the opportunities presented by more advanced networks like 5G. Operators, governments, and international organizations are collaborating to invest in infrastructure, build supportive regulatory frameworks, and raise awareness among consumers about the benefits of implementing newer technologies.
Nevertheless, the path toward sunset acceleration is long and complex. It requires a carefully orchestrated approach that not only focuses on technology upgrades but also considers the socioeconomic realities of each unique market. This includes ensuring affordable access to advanced services, developing digital skills among the population, and supporting local businesses in leveraging these technologies.
As we navigate this transformative era in telecommunications, the frequency of communicated shutdowns of networks is escalating (see Figure 2). Operators worldwide are increasingly acknowledging the need to optimize their network operations and drive cost efficiencies. And yet, while the intention to expedite the sunset of outdated infrastructure is gaining momentum, the timeline for this monumental shift remains protracted.
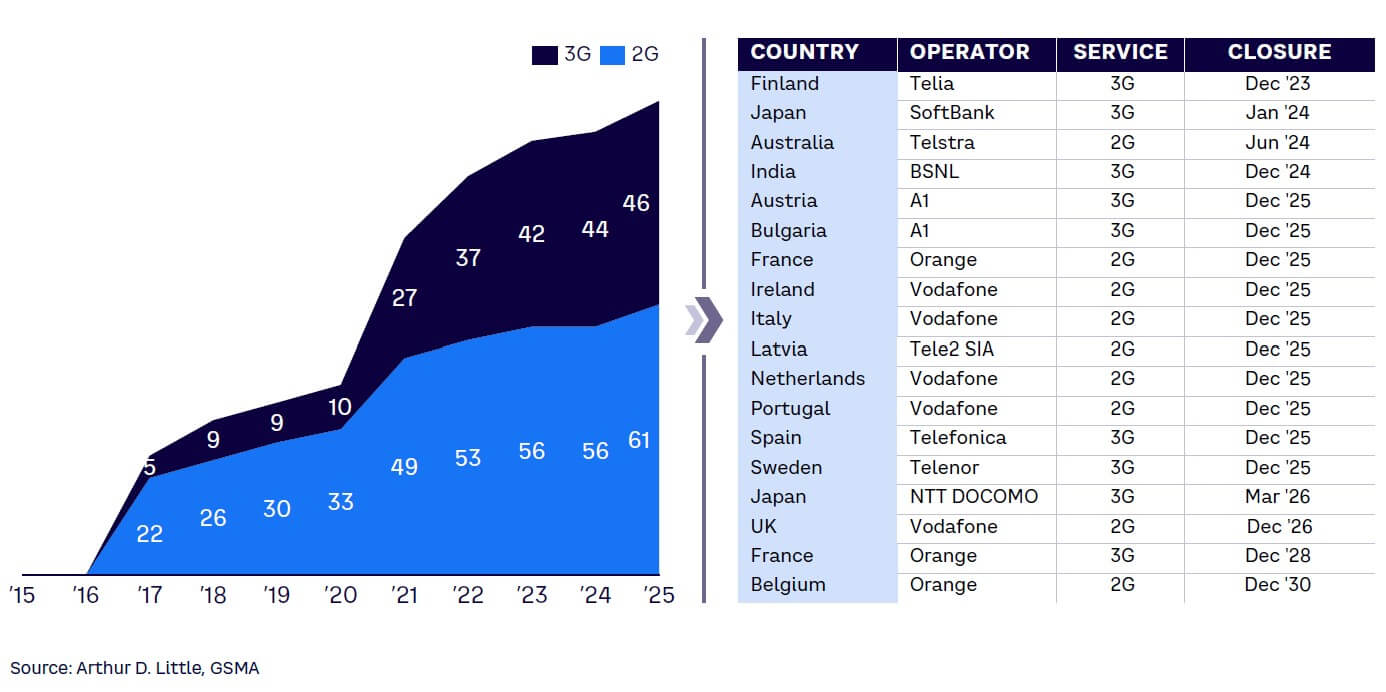
This extended timeline reflects the complexity of shutting down mobile networks and transitioning to advanced infrastructures. While the benefits are clear — enhanced network performance, cost reductions, improved customer experience, and the potential for new services and revenue streams — the process itself is multifaceted and challenging. Operators must manage multiple interdependent factors, including technical, regulatory, and customer-related elements. Technical considerations encompass the need to ensure network stability and the quality of service during the transition, while simultaneously deploying and scaling up newer technologies. Operators also need to comply with regulatory requirements regarding service continuity and customer communications, which often requires negotiation with authorities to align on shutdown timelines.
Most crucially, operators need to manage the impact of the new technology on their customers. This involves communicating the changes to them clearly and proactively, offering support as they shift to new services, and addressing any service disruptions or customer concerns that arise during the process. This customer-centric approach is vital in maintaining customer trust and satisfaction and in seizing the opportunity to upgrade customers to higher-value plans and services.
While the number of communicated shutdowns is rising, the journey toward a modern telecom landscape remains a marathon, not a sprint. It necessitates a strategic, methodical approach that balances the ambition to accelerate progress with the need to manage complexity and customer impact. As operators continue to navigate this path, their success will be defined not only by the pace of change, but also by their ability to maintain network quality, satisfy customers, and unlock new opportunities in the process.
CUSTOMER MIGRATION ACCELERATION PROGRAM BENEFITS
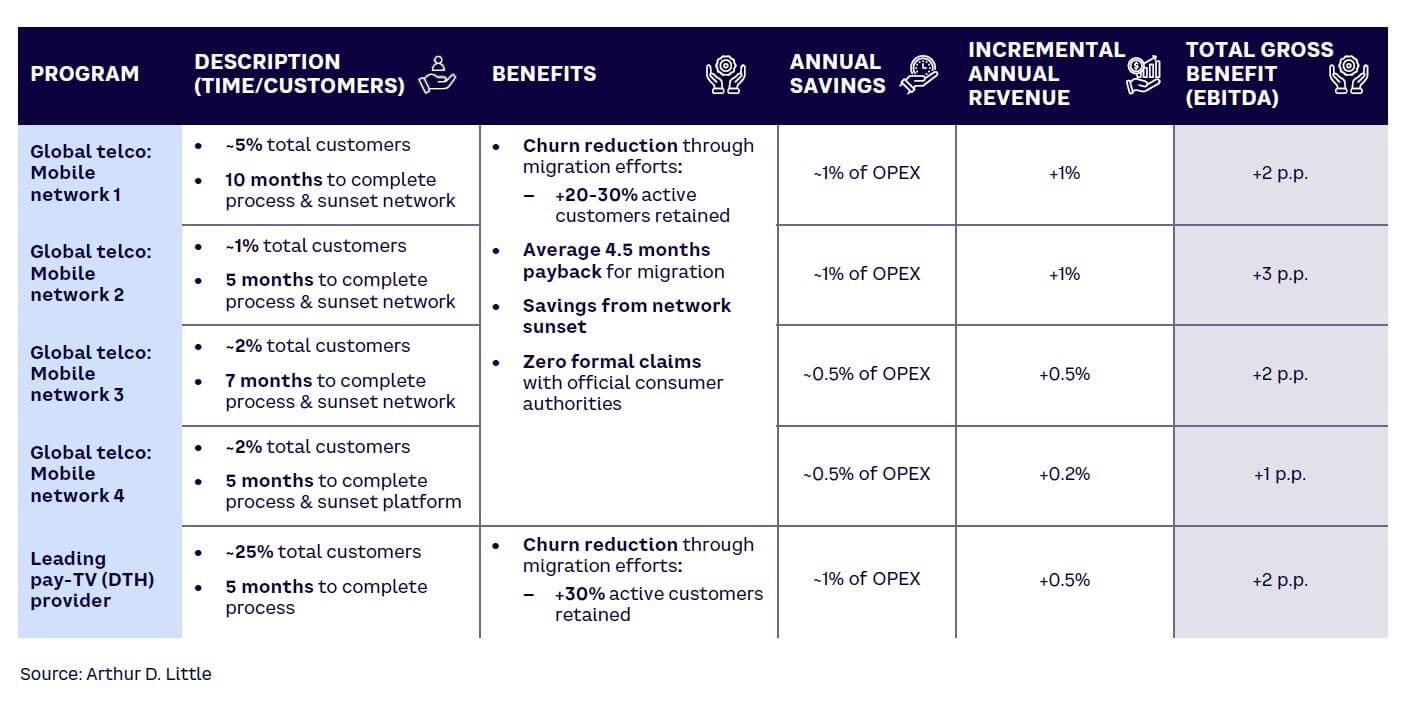
A customer migration acceleration program strategically phases out the use of legacy networks and expedites advanced technology adoption. It can serve as a significant catalyst for a telecom network operator, ushering in transformative operational, financial, and customer-centric benefits (see Figure 3). By hastening the process of closing old networks to make room for newer technologies, operators can reduce the burdensome maintenance costs that accompany outdated systems. The resulting financial efficiency allows for the reallocation of resources toward innovative, advanced infrastructure, thereby enhancing network performance and opening doors for cutting-edge services.
Furthermore, advanced networks offer a superior user experience: improved connectivity speed, lower latency, and increased reliability, which strengthens customer satisfaction and loyalty.
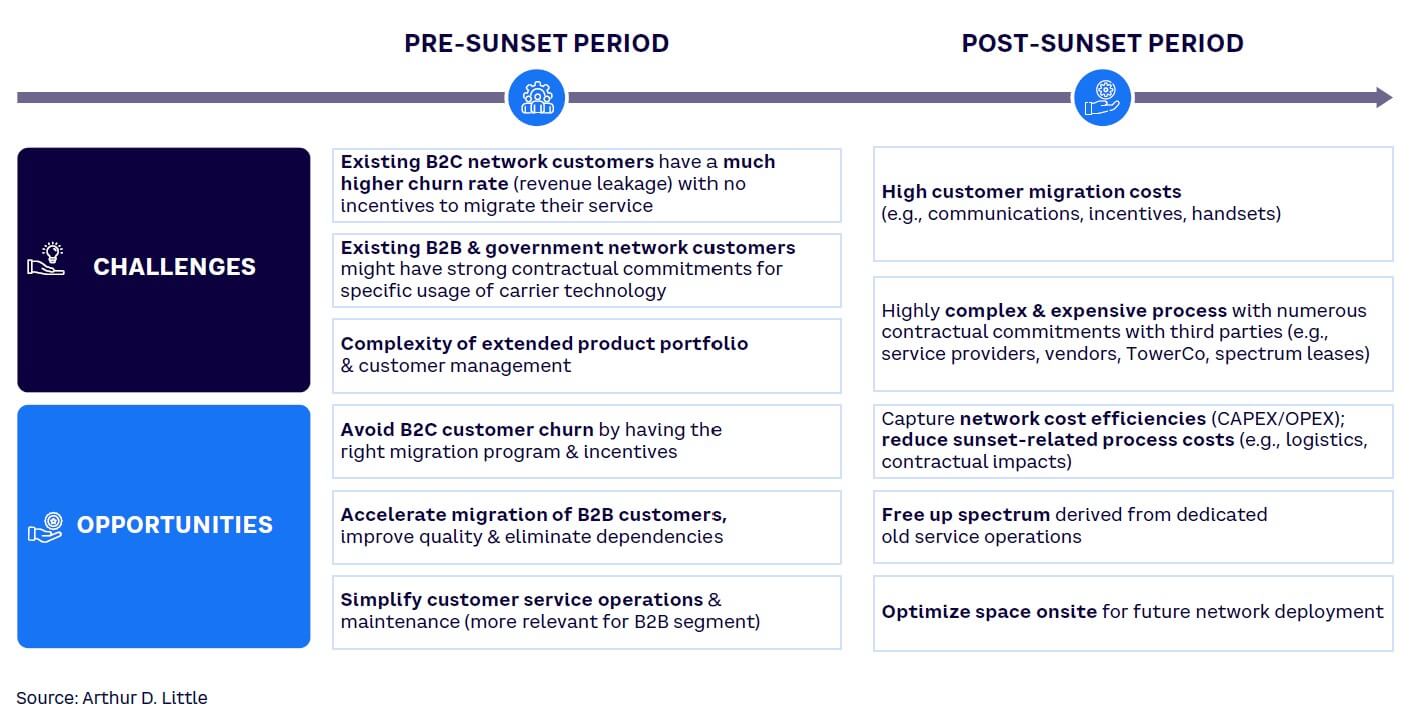
Incorporating energy efficiency into new networks as part of the transition process highlights the operator’s commitment to sustainability, reinforcing its position as a responsible steward in a world increasingly conscious of environmental impacts. Thus, a well-executed customer migration acceleration program puts operators in a position to thrive in the swiftly changing telecom industry, paving the way for operational excellence, cost savings, elevated customer experiences, and environmental stewardship.
CUSTOMER MIGRATION PLAYBOOK
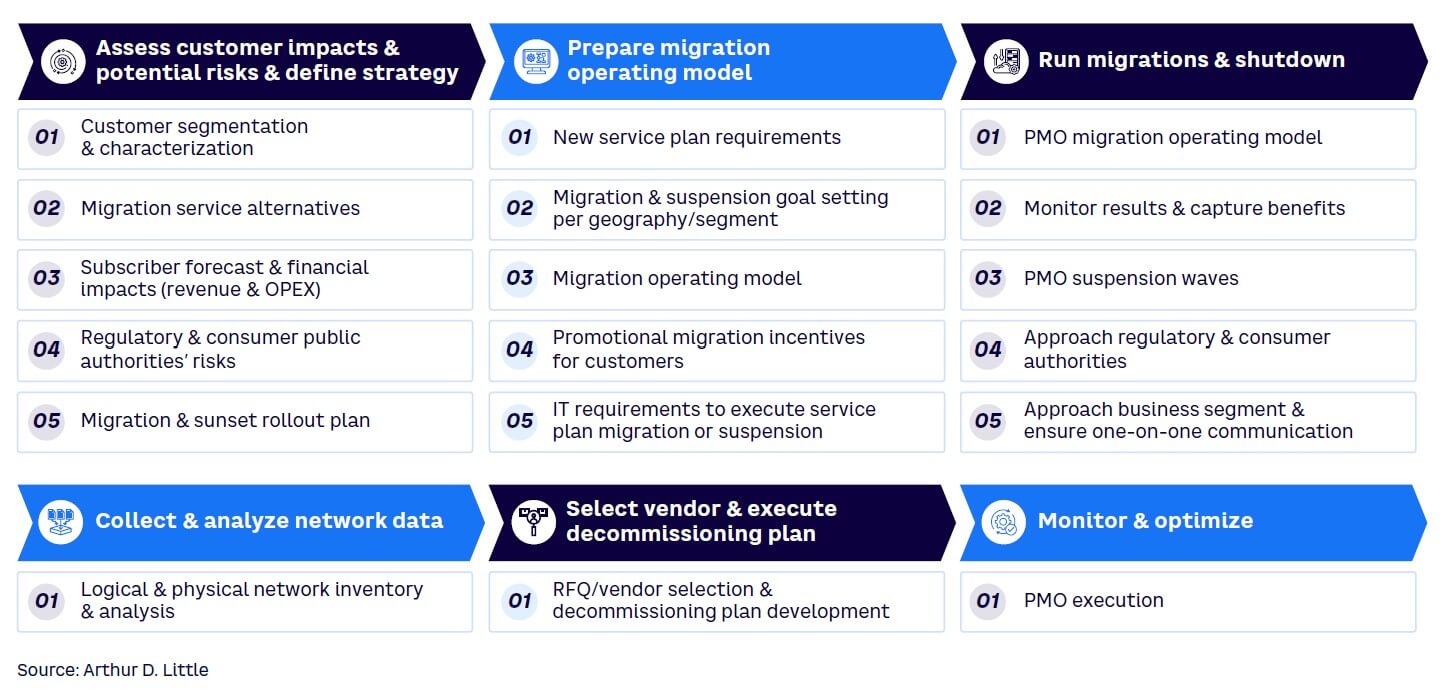
A customer migration “playbook” offers a concise approach to facilitating customer migration and expediting the switch to new technologies. First, a thorough planning stage establishes the roadmap, balancing technical, financial, and customer considerations. Next, a proactive communications strategy ensures customers are well-informed, supported, and encouraged to transition to advanced services. Finally, executing the shutdown involves meticulous management to ensure service continuity and to address any emerging customer concerns. As Figure 4 illustrates, a playbook can provide operators with a structured, customer-centric blueprint to navigate the complex journey of future network customer migration acceleration as technology evolves:
-
Define strategy. This initial stage involves assessing customer impacts and potential risks. Conducting a careful audit of existing infrastructure and customer bases, scrutinizing efficiency and costs, and identifying potential risk and opportunity will offer guidance for subsequent stages.
-
Prepare migration operating model. A detailed sunset roadmap based on knowledge gained during the assessment provides a clear path toward the intended goal. The roadmap should outline timelines, milestones, risk management strategies, and contingency plans.
-
Run migrations and shutdown. This stage helps manage expectations and maintain customer trust during transition. A comprehensive customer migration program offers customers an affordable, accessible option for maintaining service. Efforts focus on avoiding customer complaints and surpassing expectations. Stakeholder communication should be consistent and transparent and include customers, employees, and partners.
-
Collect and analyze network data. This process includes logical and physical network inventory and analysis.
-
Select vendor and execute decommissioning plan. This stage involves shutting down old systems and integrating new technologies. It’s best to complete this task in phases to minimize service disruptions.
-
Monitor and optimize. Once new systems are operational, they will require continuous monitoring and optimization to ensure delivery of anticipated benefits. Unforeseen issues are identified and addressed, and processes are refined for improve efficiency.
VALUE EQUATION OF CUSTOMER MIGRATION ACCELERATION
As we dissect the mechanics of moving from old networks to advanced infrastructure in the telecom industry, a fundamental element emerges: the value equation of the transition process. The crux of this equation revolves around the net present value (NPV) of the program. In the context of a network transition, NPV is determined by the current technological cost, the potential for customer loss, the opportunity cost, and additional factors. However, the time variable increases the complexity of the value equation.
Timing is integral to the success of the changeover. Specifically, optimizing NPV relies on deciding when to initiate and when to complete the transition. If an operator decreases the initiation period by a year and compresses the rest of the process by several months, NPV could potentially increase significantly. However, determining the optimal timing for the transition is a complex puzzle involving several factors:
-
Supplier and customer obligations. Telecom operators often have existing contracts with equipment suppliers and service agreements with customers that need to be honored. Violating these obligations could lead to financial penalties and reputational damage.
-
Economic impacts. The broader economic environment influences the timing decision. For instance, operators might defer the transition during a downturn due to budget constraints or uncertain ROI.
-
Regulatory considerations. The telecom industry is heavily regulated; any significant infrastructure change often requires regulatory approval, which can complicate timing.
-
Transition process constraints. Revamping projects can be time-consuming, requiring substantial planning, implementation, and testing. Accelerating this process too rapidly could risk the quality of the transition and jeopardize network reliability and customer satisfaction.
Given these complexities, a well-devised holistic customer migration acceleration program becomes pivotal in overcoming these limitations and optimizing the NPV of the process. Such a program could entail strategic negotiation with suppliers for flexible contracts, robust communications strategies to minimize customer churn, phased transition plans to maintain service quality, and active engagement with regulators to expedite approvals (see Figure 5).
The changeover from outdated networks to advanced infrastructure is not just a technological shift; it’s a comprehensive strategic process that requires meticulous planning and execution. By understanding and optimizing the value equation of the process, telecom operators can navigate the complex puzzle of transition timing and strike a balance between technological advancement, customer satisfaction, and financial viability. If they succeed, they will unlock substantial value and firmly position themselves in the telecom industry of the future.
THE CUSTOMER MIGRATION JOURNEY
As telecommunication technology evolves from traditional to cutting-edge, crafting a thorough customer migration strategy and steering it successfully is key. Ideally, the shift to advanced systems should be as intuitive and frictionless as possible for customers.
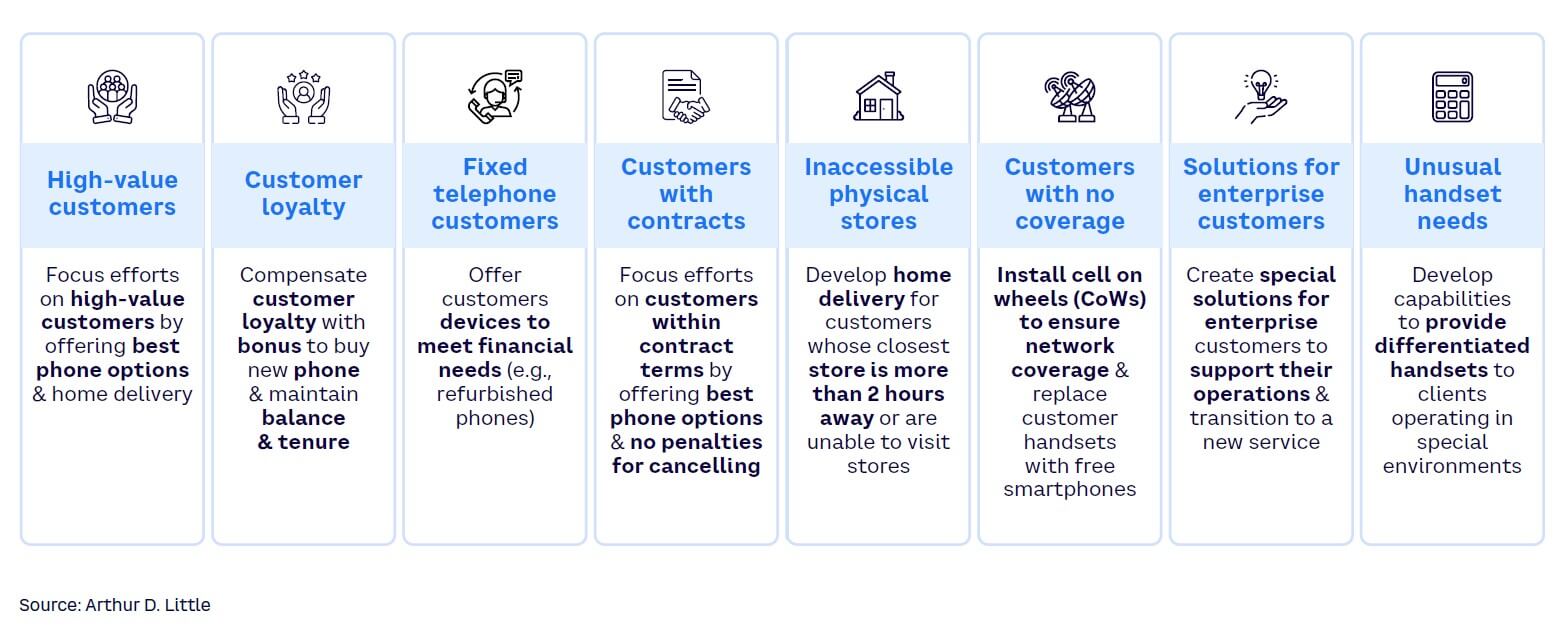
Knowledge of the customer base forms the bedrock of a successful migration strategy; each customer is unique and thus demands a different approach. Organizing the customer base into manageable groups based on demographics, usage behaviors, and preferences offers key insights that can shape a more targeted migration plan.
But segmentation is just the first step. Detailed characterization helps to truly understand each customer group. This involves delving deep into their specific needs, how they perceive the transition, and most importantly, how ready they are to embrace advances in telecommunications.
A clear picture of the customer base can facilitate scheduling and prioritizing the migration, with factors such as readiness for change, network load impact, and business considerations driving the decisions. The segmentation and characterization exercise should culminate in the creation of unique offers for each customer group. Crafting personalized incentives to motivate early transition, bundling new features with packages, and/or designing loyalty programs for longtime customers all potentially add value.
However, a migration strategy requires clear forecasts of the customer base post-migration. These predictions feed into planning network capacity, allocating resources, and financial forecasting. This brings us to a critical part of the strategy: understanding the financial impacts. This relies on having a clear-eyed view of the direct costs, the effect of customer churn, and the potential revenue uplift from the new services now possible thanks to the advanced systems. While the migration strategy forms the blueprint, the execution brings it to life. The cornerstone is setting up effective tools and channels to facilitate migration, including customer self-service portals that provide access to dedicated customer support teams.
Effective communication can make or break the migration plan. Customers need to be aware of every aspect of the migration — what it entails, how it will benefit them, and most importantly, the potential for service interruptions. This communication plan should evolve based on customer feedback and changing behaviors (see Figure 6).
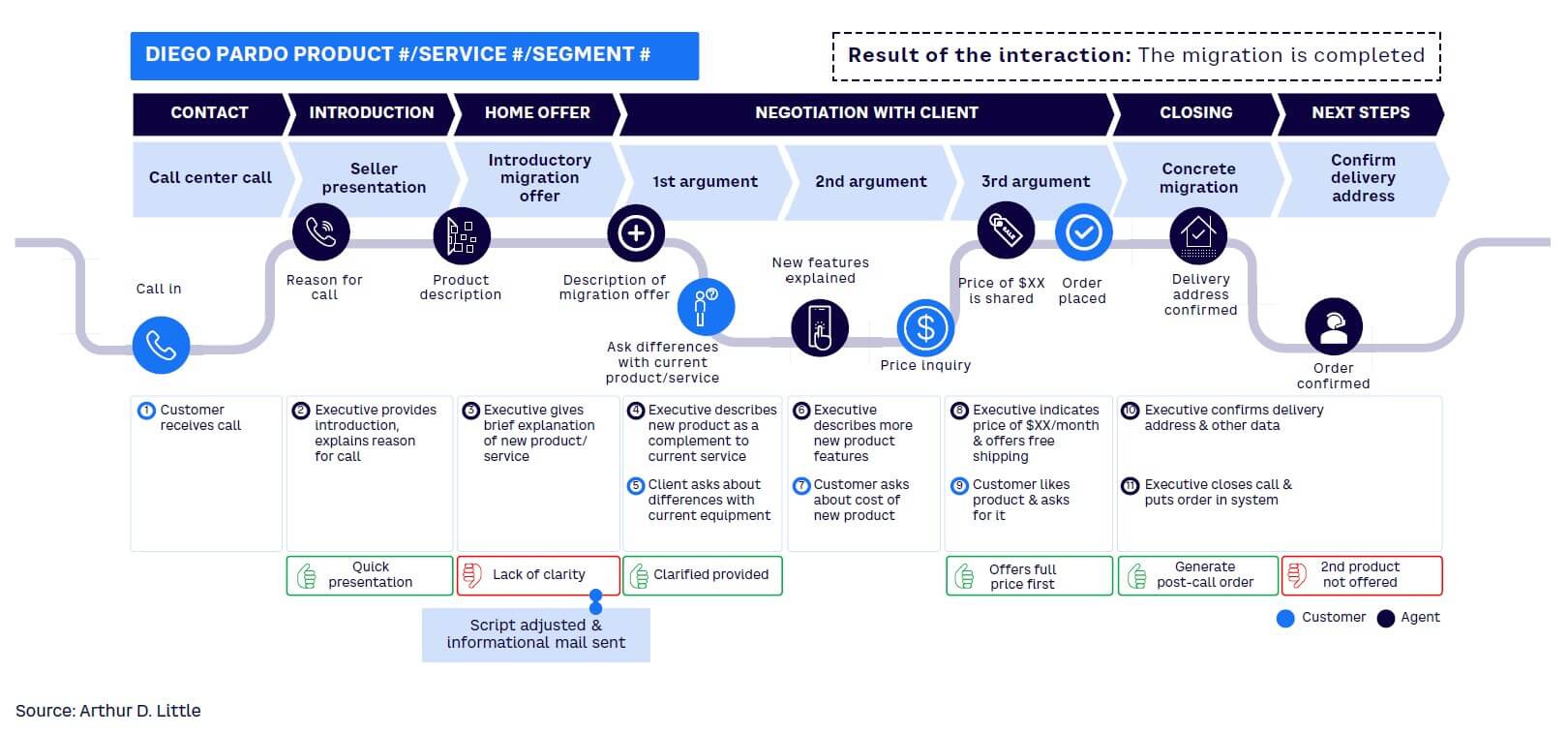
Closely monitoring progress is critical to the migration process. This involves tracking the number of successfully migrated customers, the rate of customer churn, and customer satisfaction scores. Studying these metrics can help measure success against planned milestones and identify any potential issues; the strategy can be tweaked as needed.
Preparing for the future is not just about having the most technologically advanced telecom systems; it is about ensuring a seamless, customer-centric transition, one that does not disrupt the customer experience but rather enhances it, opening new avenues for service improvement and revenue generation.
FUTURE-READY TELECOM LANDSCAPE
The transition to advanced infrastructure holds the promise of a future-ready telecom landscape, which gives operators the ability to adapt, innovate, and offer unique services. Executing a program that uses a systematic, wave-like structure of migrations and suspensions minimizes disruptions and facilitates adequate support, ensuring a seamless and customer-centric process (see Figure 7). This customer-oriented approach is designed to maintain service and may even enhance user experience throughout the shift.
Furthermore, telecom operators can significantly reduce their operating costs and environmental footprint by phasing out power-hungry, space-consuming old systems. The adoption of advanced, energy-efficient networks will enhance the sector’s sustainability profile, aligning it with broader global goals for carbon reduction and sustainable development.
Conclusion
EMBRACING DAWN OF A NEW TELECOM ERA
The transition to advanced infrastructures like 5G has ushered in a transformative era. Future success hinges on three pivotal components:
-
Advanced infrastructure — upgrading to sophisticated networks that support innovative services
-
Agile business models — adapting swiftly to market dynamics, emphasizing innovation and being receptive to feedback
-
Customer-centric approach — personalizing offerings, employing analytics, and ensuring superior experiences
This shift unlocks a world that brims with opportunities, minimizes boundaries, and maximizes potential. The telecom sector is poised for unprecedented growth that melds innovation and efficiency, and the industry must gear up for this bright horizon. While the journey might be long, the destination — a future where everyone, irrespective of geography, can access and benefit from advanced telecommunications — is worth the effort. The challenge in these regions offers an opportunity to leapfrog traditional development pathways to build a more inclusive, connected, and prosperous digital future.





